PRESENTATION
The Theory
of General Relativity introduces the idea of validating the possibility that
relative movements between bodies can be carried out at accelerated speeds. In
this essay we will demostrate that this idea can be classified as science
fiction. We could say that he exposes an absurd argument as long as the Theory
“comes out”. We will show that this argument that is called the Equivalence Principle
is a fallacy.
To carry
out our criticism we have used the book by A. Einstein entitled: "On the
theory of special and general relativity" (Ediciones Altaya S.A. February
1999). The transcriptions we
make of this book are written in quotation marks and italics.
In the last
paragraph of this study (Paragraph 9) we have transcribed from the
aforementioned book the mental experiment of the "elevator", which A.
Einstein uses to validate the Principle of Equivalence, the basis of the Theory
of General Relativity. We suggest the reader to read it before starting the
reading of this essay.
1.- A CRITERION
FOR ELIMINATION OF THE VALIDITY OF ACCELERATED SPEEDS IN RELATIVE MOVEMENTS
In our critique
of the elevator thought experiment, we rely on the following elimination
criteria:
Planet Earth
travels in outer space at a CONSTANT speed of 30 km/sec. In this way all bodies
and natural phenomena travel along with it at this speed. We ask ourselves:
What would happen if the Earth did not travel at a constant speed, but rather
its speed was accelerated? We can already imagine that the bodies that are
"on top" of it would slide on it, circling around this planet.
By comparison to
the aforementioned example, we cannot admit that, in the mental experiment of
the elevator, he proposes accelerated movements of a "CONTAINER", or
we will also call it a "PLATFORM", taking for granted natural
phenomena, their masses and their laws, which are the CONTENT of this PLATFORM.
In conclusion, the application of accelerated velocities to the Theory of
Relativity is NONNESS!
In the next
paragraphs we will talk about the PLATFORMS and their CONTENTS and also the
error, by the author of the aforementioned book, of making the equivalence of
results between the accelerated speed of a PLATFORM and a gravitational field,
thus believing that its effects fulfill the same purpose.
2.- A CONTRADITION OF CRITERIA
On page 18 of the
aforementioned book is written what is called the Principle of Relativity:
“If K' is a
coordinate system that moves uniformly and without rotation with respect to K,
then natural phenomena occur with respect to K' According to the same general
laws as with respect to K. “
Note, the reader,
that this Principle is referring to uniform speeds, but we believe that if the
author of the book expands his theory considering accelerated speeds, he will
have to demonstrate that the aforementioned Principle continues to be
fulfilled, which, in accordance with what was stated in the previous paragraph,
this does not happen. This is the CONTRADICTION that we highlight in the title
of this paragraph.
3.- PLATFORMS AND
CONTENTS
In some essays
that we have criticized topics of the Theory of Relativity, we have used
Mathematics to develop our study. In this study we rely on Physics. This is
true since the author of the mental experiment uses terms that must be refuted
using physical means.
Since in the
mental experiment that A. Einstein uses to justify the "postulate of
general relativity" he uses a drawer or an elevator, the first thing we
are going to comment on is the CONTAINER and the CONTENT that the
aforementioned experiment uses. The CONTAINER would be the elevator and the
CONTENT would be the Masses that it contains. But, to make our study more
general, we will call the Container "PLATFORM". With this
denomination we want to convey the idea that there are CONTENTS inside or on
top of it. For example, the "elevator" of the mental experiment is a
PLATFORM because inside it is mentioned that it has CONTENTS and, also, we can
consider the planet Earth as a PLATFORM because "above" it there are
CONTENTS. Understanding the meaning of the word PLATFORM, in the following
paragraphs we will use the word PLATFORM instead of CONTAINER.
The following
figure is intended to mean two PLATFORMS that have CONTENTS
Fig 1
On the left side
of the drawing, the "elevator" mentioned in the aforementioned mental
experiment has been represented as a PLATFORM. The Masses that are drawn, the
CONTENT, are inside the PLATFORM.
The right part of the drawing is intended to
signify a portion of the planet Earth. In this case the PLATFORM is the Earth.
The Masses, the CONTENT, is on its surface.
On both PLATFORMS
their CONTENTS travel with them at the same speed.
We repeat the
postulate that we have transcribed in the previous paragraph:
"If K' is a
coordinate system that moves uniformly and without rotation with respect to K,
then natural phenomena occur with respect to K' According to the same general laws
as with respect to K. "
To better
interpret this postulate, we say the following: The coordinate system (K`) is
also called: Mobile Reference System (SRM), and we interpret it as a PLATFORM
that moves in outer space. Within it their CONTENTS occur or are stored. These
contents are the natural phenomena that develop according to their physical
laws.
The coordinate system (K), we call it Fixed
Reference System (SRF). It is also a PLATFORM. It is an observation PLATFORM
and, in this case, immobile with respect to the (SRM). This Platform is
dedicated to the observation of the CONTENT of everything that it contains and
occurs in the (SRM) and is the position or point of reference of the (SRM).
Only as a
complement we can add the following. In the book that we take as a reference, on pages 55 and 56 he mentions:
“The
principle of physical relativity”
What does
it say:
"...when it is simply a question of
verifying or describing the movement, it is theoretically indifferent to which
reference body the movement refers to."
That is, we
can take (k´) as the Moving Reference System (SRM) with respect to (K), or this
(K) as the Moving Reference System with respect to (K´).
4.-
CONSIDERATIONS ON THE PLATFORM AND THE CONTENT IN A REAL CASE.- A SCIENCE
FICTION PLATFORM
Below we do an analysis of a PLATFORM that moves in outer space at an
accelerated speed. We
will consider as if it were a real case. Consequently, we do not consider the existence of “the rope” that A.
Einstein tells us about in his “science fiction” mental experiment. In this
real approach, we must take into account the following points:
1.- It is in the
PLATFORMS where the type of speed is identified. In the case that we are
studying, it is an accelerated speed.
2.- What is inside the PLATFORMS moves at its
speed. It is part of the whole. We cite as an example that everything on Earth
moves with it.
3.- In the
absence of acting forces, in outer space a Mass is either stationary or has a
constant speed with respect to a Fixed Reference System (SRF), (Galileo's
Principle)
Consequently:
4.- In a “real”
case, NOT science fiction, we cannot imagine the so-called PLATFORM floating in
outer space, acquiring speed increments by itself. What A. Einstein paints with
his "rope" in the thought experiment is science fiction.
ON THE OTHER HAND
5.- We consider
the mass as a CONTENT
6 .- In what
refers to the CONTENT, as we will see below, what A. Einstein calls
"Inertial Mass", is nothing more than a mass subjected to the action
of the "Mechanical Impulse"
7.- If the
generation of the inertial mass is caused by the PLATFORM, we cannot validate
compliance with the laws of nature. This is the case of the invalidity of the
First Principle (Example of the planet Earth)
8.- The CONTENT
can indeed generate an inertial Mass.
Let's talk
a little about the "entities" capable of moving on Earth. For
example: living beings, a car...
We can
consider a chain of relative movements. For example, a car is a CONTENT on
Earth. But Due to its ability to move by a Mechanical Impulse we can consider
it as a PLATFORM for its passengers, who are at the same time the Mass or
CONTENT and this car in its braking can generate an Inertial Mass.
5- THE
SO-CALLED INERTIAL MASS AS A RESULT OF THE ACTION OF THE MECHANICAL IMPULSE
We consider
Forces as active agents that act on a passive agent that we call Mass.
We remember that
according to Mechanical Physics, the expression of the "Mechanical
Impulse" is: IM=F×t , where (F) is the force that acts on a mass and (t)
the time in which this force acts.
We can apply this
principle both to the mental experiment in which the train car is used, and the
one in which the elevator is used.
First of all we
will use the example of the train wagon.
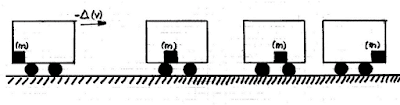
The following
drawing represents a train wagon, the PLATFORM, in which as CONTENT it carries
a mass (m). The wagon is slowing down. Its decrease in speed is represented by:
-∆(v)
This decrease in
speed is caused by a FORCE (F) that is acting for a certain time (t) braking
the wheels. That is, through the action of a MECHANICAL IMPULSE
The Mechanical
Impulse is the CAUSE whose EFFECT is that the mass (m) moves from the rear of
the wagon to the front of it. As we have already commented, the mass (m)
behaves as a passive factor and the force as an active factor.
We could do the
same approach in the event that the wagon accelerated its march. In this case,
the mass (m) would move towards the rear wall of the wagon and we could
continue considering that the so-called “inertial mass” is the behavior of the
mass as a consequence of the Mechanical Impulse. It is not a question, as A.
Einstein seems to misunderstand, “that has been transformed” into “inertial
mass”. It is always the same entity.
As we explained
at the beginning of this essay, the accelerated speeds are not valid for us to
attribute them to relative movements: "The masses on Earth do not move on
it"
6.- THE
CONCEPT OF MASS IS UNIQUE. IS AN ENTITY
The author
of the book that we are taking as a reference dedicates a lot of attention to
establishing a distinction in the concept "Mass". He makes a first distinction by calling it
Inertial Mass and Gravitational Mass, and this could be interpreted as two
different entities. But, at the end of “dizzy the partridge”, he says:
"The same quality of the body manifests
itself as inertia or as gravity" .
We say that it is
a MANIFESTATION of the MASS when a Contact Force (Traction or Compression) or
an Attraction Force acts on it. Perhaps it is a better way to interpret a
"behavior" and not attribute it to a "transformation". Let
us remember that in our last essay we already denounced that the author of the
aforementioned book seems to have liked to think about
"transmutations".
We believe that
the best way to approach relative movements with accelerated speeds is using
the ideas of: Platforms, Contents and Acting Forces.
In the
aforementioned book, on page 60, he presents a "muddy" mathematical
formula of doubtful validity. The validity of his approach seems designed so
that his answer is in accordance with certain facts and not that, from certain
facts, a mathematical formula is raised. The “certain facts are the existence
of an Inertial Mass and a Gravitational Mass.
On page 65
of the aforementioned book, his author details a mental experiment in which he
exposes the movement of a SAME MASS subjected respectively to a Traction Force
and an Attraction Force. The mental experiment exposed by A. Einstein is quite
"twisted". Perhaps, from what we will see, we could call him:
"read it, understand it, and thus he will learn to walk through a
maze"...
This experiment
only demonstrates that, in the relative movements between bodies, their
CONTENT, the Mass, can be moved using two different types of force. But, from
here we cannot deduce anything else. It is only an exposition of a cause that
produces its effect. Next, we have transcribed this thought experiment from the
aforementioned book and, then, to make it more intelligible to the reader, at
the end we have summarized its parts illustrating them with drawings. In this
experiment the author, instead of using the elevator, uses the train car again.
We transcribe the aforementioned experiment:
“… It is certainly true that the observer who
is in the wagon feels a jerk forward as a consequence of the sudden braking and
it is true that in this he notices the non-uniformity of the movement. But no one forces you to attribute
the jerk to a "real" acceleration of the wagon. You could just as well interpret the episode like
this: “My reference body (the wagon) remains constantly at rest. However,
(during the braking time there is a temporally variable gravitational field
directed forwards relative to it. Under the influence of the latter the
embankment, together with the Earth, moves non-uniformly so that its initial
velocity is directed backwards , decreases more and more. This gravitational
field is also the one that produces the pull of the observer”
As we said, to try to improve the interpretation of this text, we have divided its content graphically and into two parts:
1.- Within a
PLATFORM, which is considered a Mobile Reference System (SRM), as a consequence
of a deceleration, an Inertial Force is generated over the mass (m) that is
called Inertial Mass. This Inertial Mass is generated by braking the wagon.
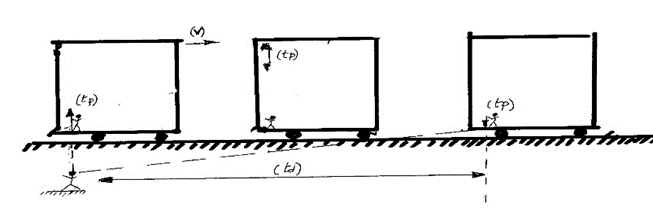
The following figure represents three phases
of advance of the train wagon in its deceleration: -∆(v) , and the movement by
inertia of the mass (m).
In this first step, the author wants to highlight that the Mass has moved by inertia or that, from what we already know, in response to a Mechanical Impulse. Thus he intends to demonstrate that what he calls Inertial Mass exists and moves.
2.- In this
second step he intends to demonstrate that “the same mass also moves in the
presence of a gravitational field. Which he will call Gravitational Mass.
Change the PLATFORM (the wagon) as a Mobile
Reference System (SRM) for that of a Fixed Reference System (SRF), and change
the concept of moving the mass by inertia in front of the wagon, for the one that
it is attracted by a field mobile gravity.
The following
figure represents three phases of the movement of a mobile gravitational field
that we have written in the previous transcript
It places this mobile gravitational field, which is moving in outer space, so we have to think, although it does not say so, that it presupposes some mobile "body" that intervenes and interacts with the mass (m) in this mobile gravitational field. .
This mobile
gravitational field is attracting and displacing forward the mass (m), which is
inside the immobile wagon. As cited in the experiment, this field increasingly
moves further away from the train carriage. Consequently, it is getting weaker.
In summary, with this mental experiment the aforementioned Physicist intends to
demonstrate that the same mass can be
It moves due to inertia (according to us as a consequence of the
mechanical impulse) and it also moves due to the effect of a gravitational
field.
Apart from
making a "science-fiction" approach, this approach does not allow us
to accept: "that since the two actions cause an accelerated movement of
the MASS, this is enough for us to accept that the" First Principle of
Relativity is fulfilled. The accelerated movement of the Mass (m) precisely denies
the fulfillment of such a Principle.
7.- THE
FALLACY OF THE PRINCIPLE OF EQUIVALENCE
The author
of the mentioned book in his mental experiment to validate the accelerated
speeds in relative movements, makes the mistake of establishing an EQUIVALENCE
between the result of submitting the MASS to the ACTION of an accelerated speed
or submitting this same MASS to the attraction of a attractive force, such as
gravity. He commits a fallacy of logical inconsistency. This is the fallacy
called “false equivalence”. We
transcribe the explanation that appears in an information medium that details
seven of the possible existing fallacies:
“False equivalence is a fallacy of logic that describes a situation
where there is an apparently logical equivalence, but in reality there is none.
This fallacy can be classified as a fallacy of inconsistency.
It hurts that the
aforementioned physicist, with the intelligence attributed to him, committed an
outrage against logic.
(NOTE: Some time
ago, in one of our books we also commented on one of these seven fallacies to
which we have referred. It is the "ad hominen" fallacy. It is about
admitting something as true by the mere fact that a person says it. person to
whom we have some consideration.
The reader should
not fall into the trap by believing the mental experiment that the
aforementioned Physicist proposed to accept the Principle of Equivalence, for
being who they say it was!)
In summary, the only EQUIVALENCE that we can
establish between the two mentioned ACTIONS is that each of them results in
MOVING the mass. But,
we ask ourselves, is this EQUIVALENCE valid for us to be able to say that one
ACTION can replace the response of the other?
Let's remember the example we gave in our first paragraph in the case of
planet Earth. The
acceleration of the PLATFORM, has as a response a sliding of its CONTENT; mass.
The other ACTION, the force of gravity, does not displace the MASS on the
PLATFORM, but attracts it towards its center. In the aforementioned ACTIONS, it
is necessary to take into account their way of ACTING. That is, the two ACTIONS
ARE NOT EQUIVALENT
8.- FACED
WITH A SCIENCE FICTION PARADOX, A RATIONAL EXAMINATION
If in our previous essay we said that the
“paradox of transmutation was very difficult to believe, in this essay, as we
have seen, we have dealt with nonsense that is difficult to accept.
To digest
and criticize the use of some mental experiments whose approach deviates from
the minimum requirements of logic, we will comment below on a graphic simile that
we have already exposed in previous essays. We call it the “Third Eye”.
Through a
graphic simile, we present a metaphor that aims to represent our observation of
a thought experiment in real life. We place ourselves outside the
"observation yard" of the MENTAL experiment and, from the outside, we
establish a PHYSICAL experiment to observe what would happen in a real case. This
is what we could deduce from our essay.
The
following figure is intended to represent this concept. The "yard" of this game is in outer
space. Consider the Elevator as the Mobile Reference System (SRM) located in
the "patio" and, also, in any situation of this "patio" the
Fixed Reference System (SRF) that observes the experiment
If we agree with everything we have analyzed, to reveal another contradiction in this mental experiment we transcribe a piece of the story that appears in the book that we take as a reference and we will discover that its content belongs to the "patio"
We
transcribe a part of the aforementioned mental experiment:
“…Is it lawful to
laugh at man and say that his conception is a mistake? I think that if we want
to be conscious, we cannot, but we must admit that his explanation does not
attack reason or known mechanical laws. Even if the crate is accelerated with respect
to the Galileo space considered first, it is possible to view it as stationary.
So we have good reasons to extend the principle of relativity to reference
bodies that are accelerated with respect to each other, and thus a powerful
argument has been gained in favor of a postulate of general relativity."
We could
put this piece of the thought experiment that we transcribe from the
aforementioned book and that aims to validate relative movements with
accelerated speeds in the mouth of the person who is outside the elevator and
in the "thought experiment yard." We create and save our criteria from outside the
“yard”. That is, from the "Third Eye"
Seen from the
Third Eye, we say that this is the science fiction argument with which we
baptize our essay. We can add that his reason leads us to consider that in the
previous reasoning he commits another fallacy of logic. It is that, with a
"FEELING" of the person-
The one that is inside the elevator tries to validate the EQUIVALENCE between the result of subjecting the MASS to the ACTION of an accelerated speed or subjecting this same MASS to the attraction of an attractive force.
9.- TRANSCRIPT OF THE ELEVATOR THOUGHT
EXPERIMENT
From the book by
A. Einstein, "On the theory of special and general relativity"
(Ediciones ALTAYA S.A. February 1999) in paragraph 20, title: "Equality
between inertial mass and gravitational mass as an argument of the postulate of
GENERAL RELATIVITY", pages 61 and 62, we transcribe the following:
"Imagine a
large piece of empty space, so far from stars and large masses that we can say
with sufficient accuracy that we are dealing with the case provided for in
Galileo's fundamental law. For this part of the universe it is then possible to
choose a Galileo reference body for which the points at rest remain at rest and
the moving points remain constantly in a uniform and rectilinear motion.As a
reference body we imagine a large drawer in the shape of a room, and we assume
that there is an observer equipped with devices for Naturally there is no
gravity on him, he has to be roped to the floor, under penalty of being thrown
to the ceiling at the slightest hit to the ground.
Suppose that in
the center of the roof of the caisson, on the outside, there is a hook with a
rope, and that a being, of which we are indifferent, begins to pull on it with
a constant force. The crate, together with the observer, begins to fly
"up" with a uniformly accelerated motion. Your speed will increase
over time...always great heights to judge everyone from another reference body
not pulling a string.
But how does the
man in the drawer judge the process? The floor of the box transmits the
acceleration pressure on the feet. Therefore, you must counteract this pressure
with the help of your legs if you do not want to measure the ground with your
body. So, you will be standing in the box like a person in any room of a house.
If you drop a body that was previously in your hand, the crate's acceleration
will stop acting on it, so it will approach the ground with an accelerated
relative motion. The observer is also convinced that the acceleration of the
body with respect to the ground is always the same great regardless of the body
that performs the experiment.
On the basis of
his knowledge of the gravitational field, as we have discussed in the last
section, the man will come to the conclusion that he is, along with the box,
within a fairly constant gravitational field. For a moment, however, you will
be surprised that the caisson does not fall into this gravitational field, but
then you discover the hook in the center of the ceiling and the tight rope
attached to it, and you correctly infer that the caisson hangs at rest in that
field.
Is it lawful to
laugh at man and say that his conception is a mistake? I think that if we want
to be conscious, we cannot, but we must admit that his explanation does not
attack reason or known mechanical laws. Even if the crate is accelerated with respect
to the Galileo space considered first, it is possible to view it as stationary.
So we have good reasons to extend the principle of relativity to reference
bodies that are accelerated relative to each other.